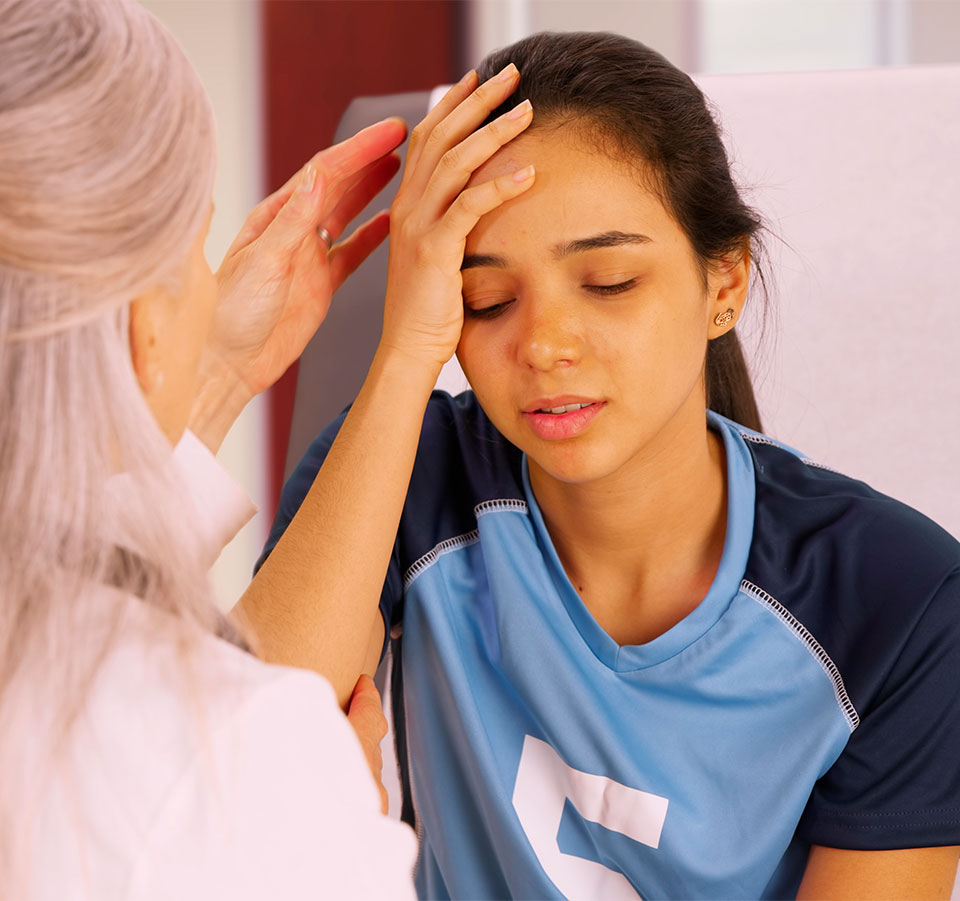
A concussion is a traumatic brain injury (TBI) that affects your brain function. The effects of this injury can be quite severe, persistent, and debilitating, and can include headaches and problems with concentration, memory, balance, and coordination. Other symptoms include confusion, nausea, brain fog, vomiting, sleep issues, sensitivity to light and loud noises, excessive fatigue, dizziness, and ringing in the ears (tinnitus). TBI’s account for 30% of all injury related deaths. The most at-risk individuals are ages 0-4, 15-19, and 75+ with the number one cause due to falls.
Concussions are often the result of a bump, jolt, or blow to the head, or violent shaking of the head and body. The forward and backward motion of the neck during a car crash, fall, or sports injury—known as whiplash—is a perfect example of this. This sudden movement can cause the brain to bounce around or twist in the skull, creating chemical changes in the brain; at times, this results in stretching or damaging of the brain cells.